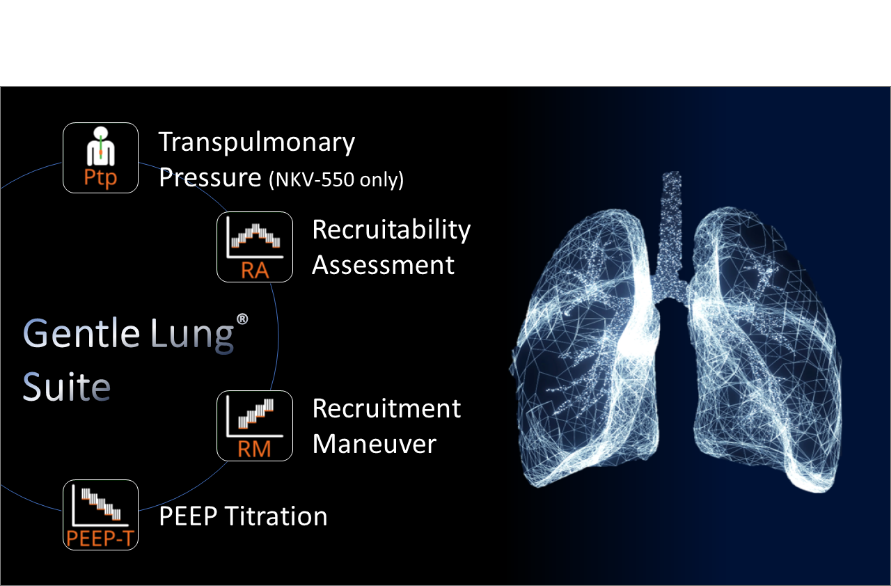
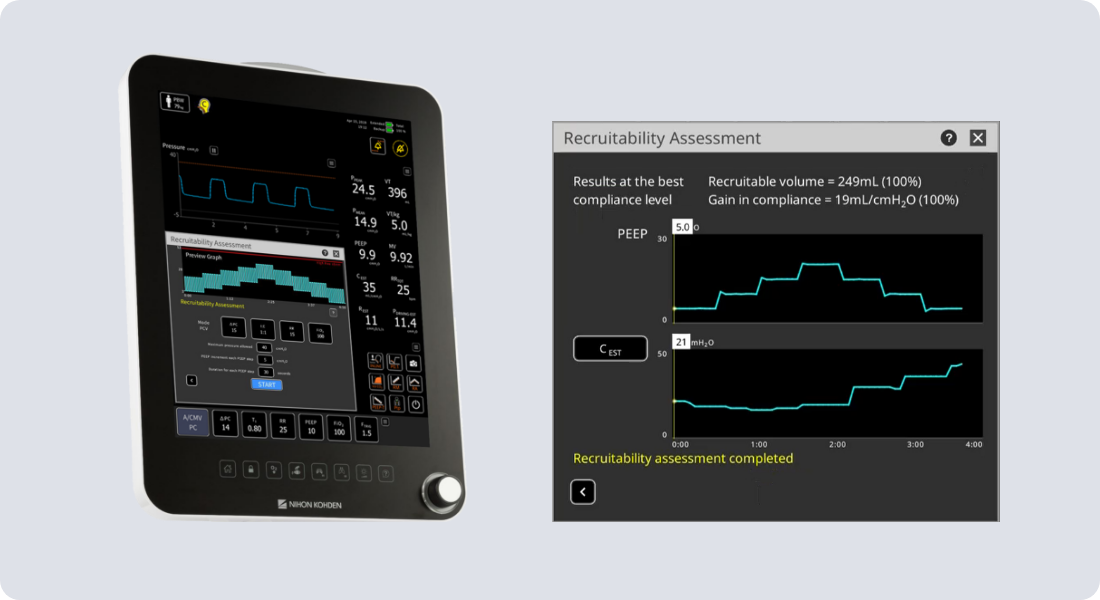
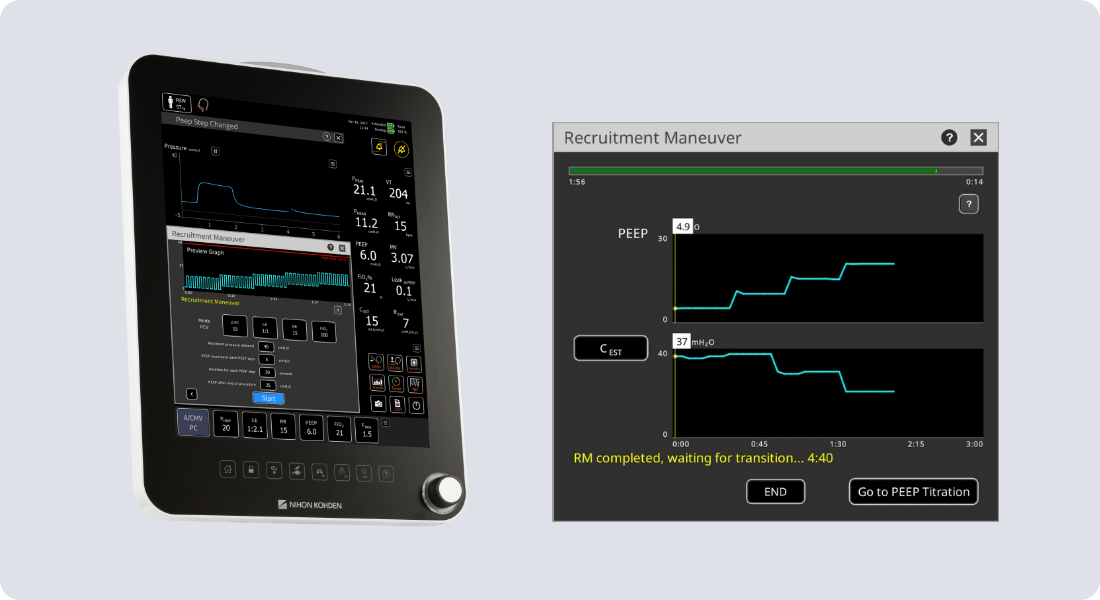
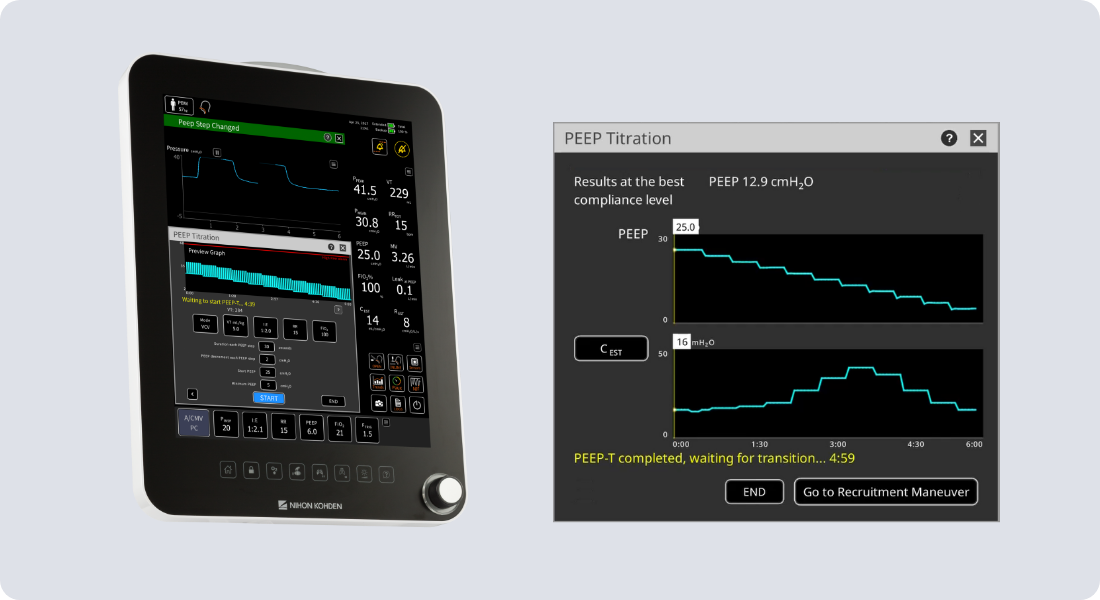
Gentle Lung® Suite

Gentle Lung
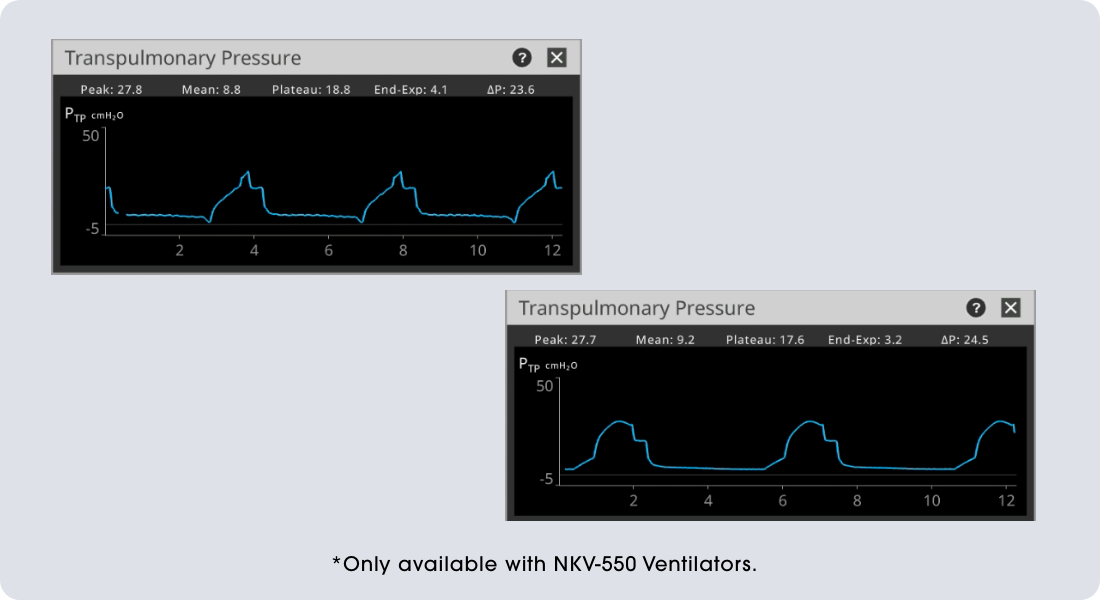
Patients receiving mechanical ventilation may suffer from ventilator-induced lung injury. This may be caused by inappropriate tidal volume1, inappropriate driving pressure2, and inappropriate PEEP3.
Guided Solutions
Lung protective ventilation is a well-established practice not only in ARDS patients but also in postoperative patients4. Gentle Lung Suite provides guided tools for individualized lung protective strategies
1 The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. Ventilation with Lower Tidal Volumes as Compared with Traditional Tidal Volumes for Acute Lung Injury and the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2000 Feb;342(18):1301–8.
2 Amato MBP, Meade MO, Slutsky AS, Brochard L, Costa ELV, Schoenfeld DA, et al. Driving Pressure and Survival in the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(8):747–55.
3 Briel M, Meade M, Mercat A, Brower RG, Talmor D, Walter SD, et al. Higher vs lower positive end-expiratory pressure in patients with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: Systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2010;303(9):865–73.
4 Fumagalli J, Santiago RRS, Teggia Droghi M, Zhang C, Fintelmann FJ, Troschel FM, et al. Lung Recruitment in Obese Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Anesthesiology. 2019;130(5):791–803.
5 Talmor D, Sarge T, Malhotra A, O’Donnell CR, Ritz R, Lisbon A, et al. Mechanical ventilation guided by esophageal pressure in acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2008 Nov 13;359(20):2095–104.